Pilot Case Study
End-To-End Electronic Support Improves Patient Access for Specialty Medications
| Austin Raper, Ph.D.
AMP: Access for More Patients™ Reduces Time-To-Therapy by 27%
Relative to traditional pharmaceuticals, access requirements for specialty medications are more numerous, time-consuming and complicated, with patients often struggling to coordinate therapy on their own. While manufacturer-sponsored hub services exist to help patients and providers fulfill necessary steps to start specialty therapies, manual inefficiencies and misaligned incentives within the traditional hub model limit effectiveness of support. To address these challenges and help patients get the medications they need, an electronic platform for support services was developed – AMP: Access for More Patients™ (AMP). Within two months of operation for a specialty medication in the neurology therapeutic class, AMP achieved widespread provider adoption, marked reduction in completion time for administrative processes and significant improvement in time-to-therapy for patients.
Study Highlights
- Patients enrolled in AMP experienced a 27% reduction in time-to-therapy relative to industry standard
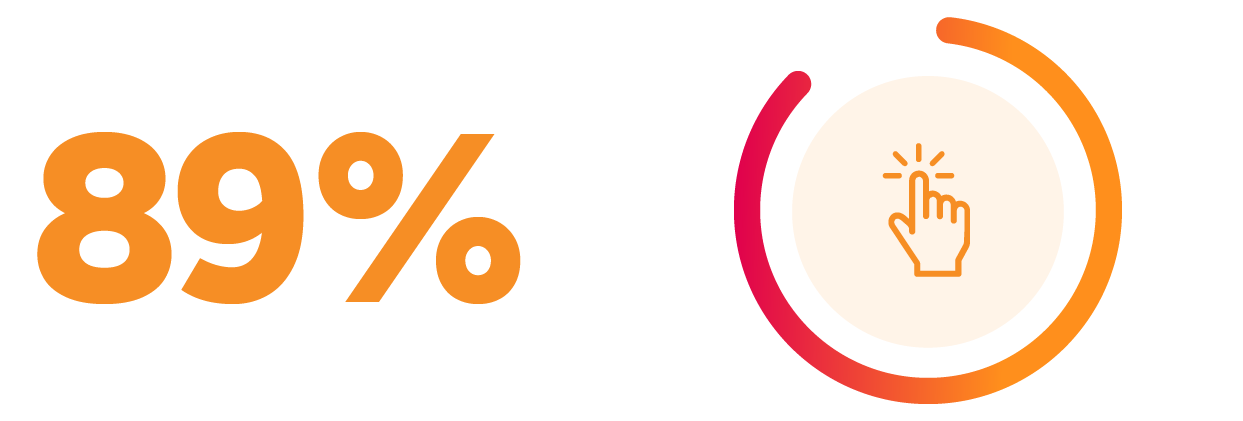
- Adoption of AMP by prospective providers reached 89% in two-months’ time
- AMP achieved a 92% enrollment completion rate with 48% of enrollments completed electronically
Health Care Need
Specialty Medications Are Linked With Health Care Complexity
Despite representing ~2 percent of current prescription volume, specialty medications are on track to account for 47 percent of pharmacy revenues by 2022 (i.e., projected $248 billion of $528 billion).1,2 These high-complexity, high-cost therapies often require unique administration (e.g., nebulizer, injection, infusion), consistent patient monitoring through lab tests or regular checkups and time-intensive upfront processes, including enrollment documentation, benefit verification, FDA-mandated risk evaluation and mitigation strategies (REMS) and prior authorization (PA). Navigating through all these requirements is challenging for health care experts, let alone inexperienced patients.
Patient Burden
As a result of these added layers of complexity, it can be difficult for patients to access and remain adherent to their prescribed specialty therapies. In fact, research shows that specialty medications are more likely to be abandoned relative to traditional pharmaceuticals, with 27 percent of patients failing to start therapy in some cases– despite it being prescribed by their doctor and approved by their insurance.3
For patients in the neurology therapeutic area, access challenges can contribute to medications adherence rates as low as 41 percent in some instances.4 Without expert support, neurology patients can find themselves coordinating all steps required to start therapy on their own – with many describing this as a full-time job.5 A 10-member patient advisory board for a specific neurological condition confirmed that patients feel significant burden from the process required to start specialty medications.6 On average, these patients claimed to have made 30 or more phone calls to health care stakeholders and spent many hours personally coordinating their own care.6
Provider Burden
Access challenges for specialty medications extend to providers as well. In a recent survey to over 500 health care providers, fewer than one-third expressed satisfaction with the prescribing process for specialty medications – citing multiple hours each week spent on completing documentation for patients to start therapy, confusion about where to send specialty prescriptions and uncertainty about which enrollment documents to complete.7
As a result, over two-thirds of providers switch to an alternative medication if they encounter a barrier during the specialty prescribing process7 – even though the original therapy may have been their preferred choice.
Limitations of Traditional Support Services
As specialty medications are associated with significant access barriers, manufacturers and third-party vendors offer hub support services to guide patients through challenges and fulfill all requirements necessary to begin therapy. Manufacturers often rely on providers to communicate availability of hub support,8 but this information rarely reaches patients. Survey research indicates that only one in five patients are aware of hub support.8
Beyond these patient intake dilemmas, traditional hub support services rely on outdated communications channels (e.g., phone calls and faxes) to fulfill enrollment criteria and start patients on therapy, which may require upwards of 70 touchpoints among health care stakeholders.9 As a result, time-to-therapy can extend eight weeks from when a prescription is written even with hub support.5,10
Compounding this issue, traditional hub service providers typically operate based on a full-time employee (FTE) cost structure10 so there is little incentive to increase productivity and efficiency. For the FTE model, as more patients are enrolled in a hub program, more FTEs are needed to complete corresponding case work. As a result, more employees must be hired to keep up with the increased workload such that total program costs can rise precipitously.
About AMP
AMP, a customizable, electronic platform for hub support services, was created by CoverMyMeds and RxCrossroads by McKesson in response to deficiencies of the traditional hub model and the needs of patients and providers. With AMP, patient intake can be funneled through the point of prescribing (i.e., while the patient is still at the doctor’s office) and health care stakeholders are able to coordinate enrollment steps and access requirements for patients through a centralized online portal. Through the portal, information can be shared in real-time and each stakeholder is notified when action is required on their part. In this report, we describe results from a two-month pilot study where AMP was implemented for a specialty medication in the neurology therapeutic area to positively impact patients with a 27 percent reduction in time-to-therapy.

Patient Intake at the Point of Prescribing: As e-prescriptions for specialty medications can trigger enrollment into AMP, potentially all patients have access to support services. If medications are manually prescribed, enrollment can be started directly in the specialty web portal. Traditional enrollment via fax is also available.
Clear Path to Viral Adoption: AMP was developed as an extension of the CoverMyMeds provider portal with an existing user base of over 700,000 providers. For some therapeutic areas, over 90 percent of prospective national provider identifiers (NPIs) have accessed the portal in the last 90 days. For this study, there was 94 percent overlap between the manufacturer’s prospective NPI list and regular CoverMyMeds portal users.
Electronic Processes: Patient enrollment and consent, benefits investigation and verification (BI/BV), financial assistance, prior authorization (PA) and scheduling lab tests can be requested or completed electronically to help decrease time-to-therapy for patients.
Centralized Access: The CoverMyMeds portal can serve as the single access point for specialty medications for all health care stakeholders. Through an online dashboard, patient case status and progress can be tracked, giving providers, patient service coordinators and case managers a longitudinal view of their patient’s journey.
Exception Management: When a patient case deviates from the standardized AMP workflow, expert case managers are on standby to fulfill any outstanding tasks for starting therapy.
Ongoing Adherence Support: Patient data is continuously tracked and monitored for comprehensive outcomes reporting with added support from RxCrossroads by McKesson. Tech-enabled tools and programs may be used to help patients remain on therapy.
Study Results
During a two-month time period, AMP was evaluated on several key metrics indicative of program adoption, efficiency and overall performance.
Enrollment
Over 1,248 patients were enrolled in AMP services by 501 unique NPIs
- Of providers on the initial, prospective NPI list, 89 percent enrolled patients into AMP services (i.e., 501 out of 562 NPIs)
-
67 provider locations across the US were identified as centers of excellence (COE) within the neurology therapeutic class. Patient enrollment into AMP services was initiated from 90 percent of these locations (i.e., 60 out of 67 COEs)
-
Of NPIs that enrolled patients into AMP services, 46 percent enrolled more than one patient during the study period
-
92 percent enrollment completion rate relative to 50 percent industry standard for traditional hubs
48 percent of enrollment forms were submitted electronically instead of by fax compared to the less than 10 percent industry standard.
- Electronic enrollment completed 38 percent faster than fax enrollments
- On average, enrollment was completed within 23 business hours

Burden Relief and Exception Management
When calls to health care stakeholders were necessary to drive case progress, AMP case managers were efficient in identifying what information was needed and who should be contacted – helping to avoid preventable, burdensome calls to providers and patients.
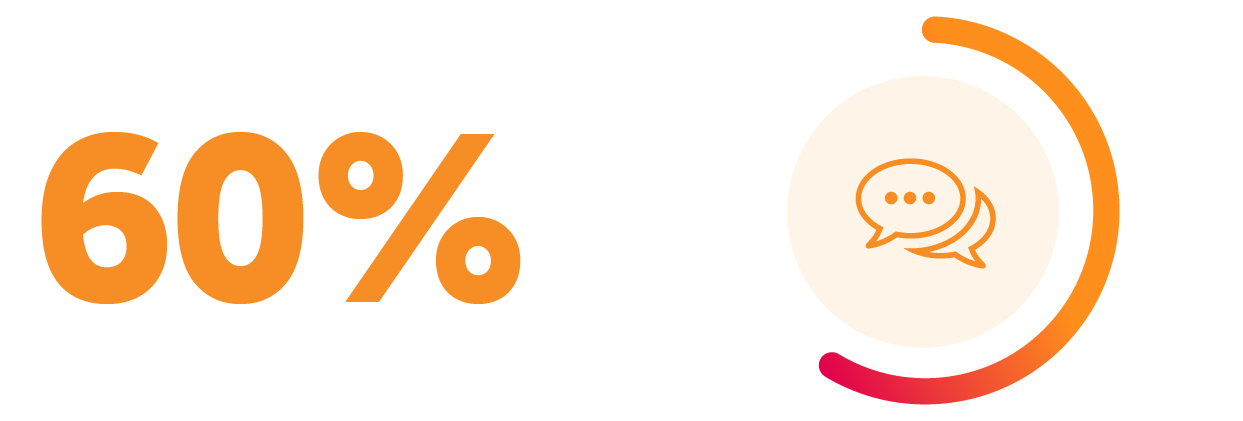
AMP case managers were successful in gathering the needed information to resolve outstanding case issues for approximately 60 percent of all phone call attempts. The remaining 40 percent of phone call attempts were simply not answered at the time of the call.
Benefits Investigation and Verification
-
Benefits verification completed in 1.2 days on average
-
Benefits investigation completed within eight days
-
For 85 percent of patients, benefits information was retrieved within 37 seconds through electronic benefits verification technology (eBV)
Prior Authorization
-
98 percent of completed PA requests were submitted within one business day
-
60 percent of submitted PA requests were approved
-
For denied PA requests, 63 percent of appeals were approved
-
58-hour average turnaround time for PA request determinations (from initiation to completion)
Time-To-Therapy
- BI/BV/PA completed within 11 days* on average, as compared to weeks for traditional specialty workflows11
- 20 days – average time from enrollment completion to when a signal is triggered for prescription dispense

- For this particular neurology product, lab tests are required before patients can begin therapy. AMP schedules labs on behalf of patients. On average, the median time between when an appointment for a lab test was scheduled to when it occurred was 14 days.^
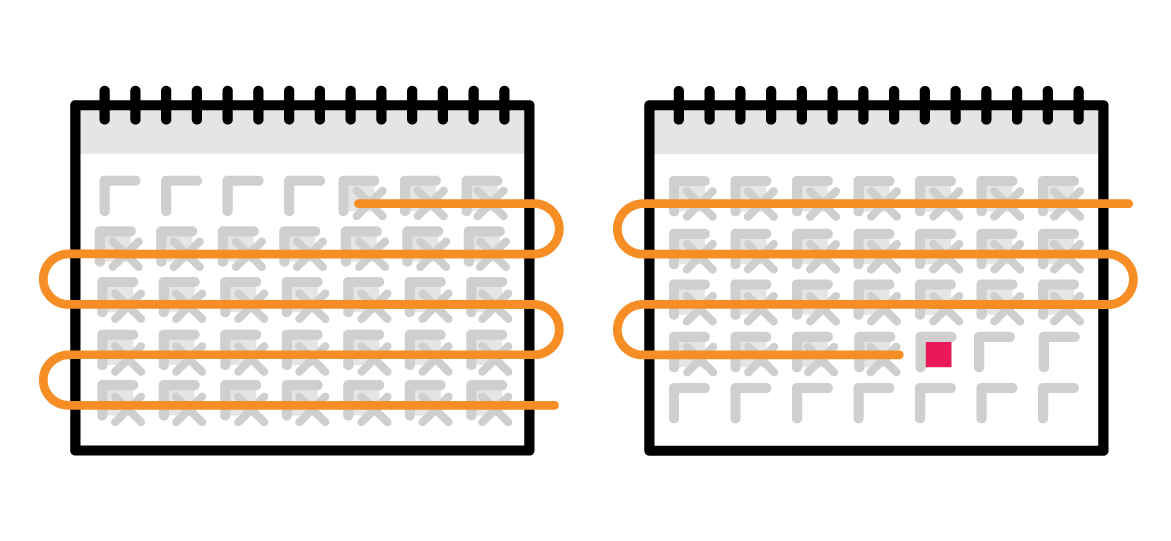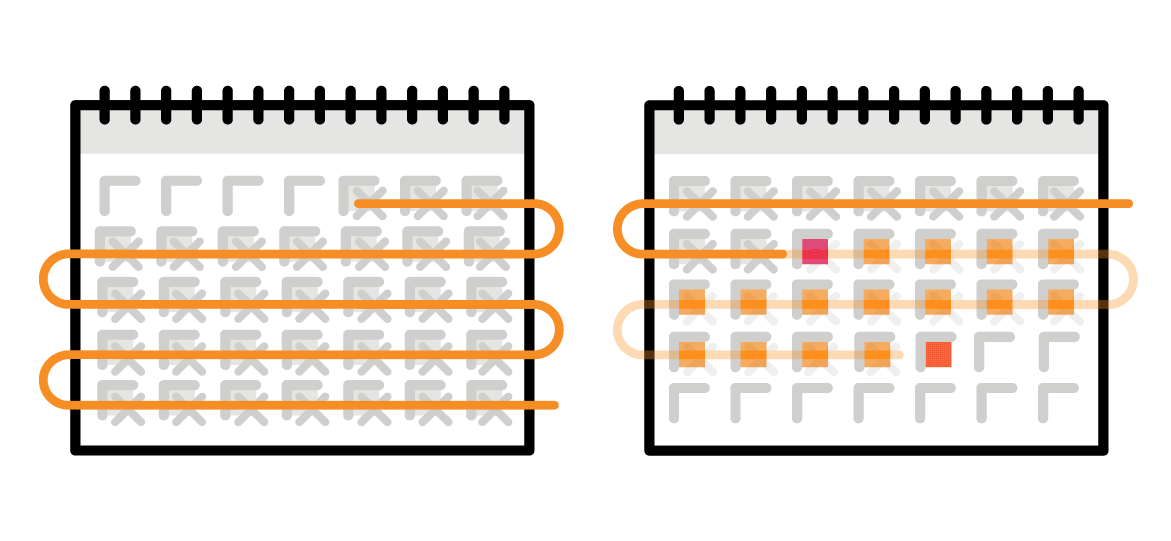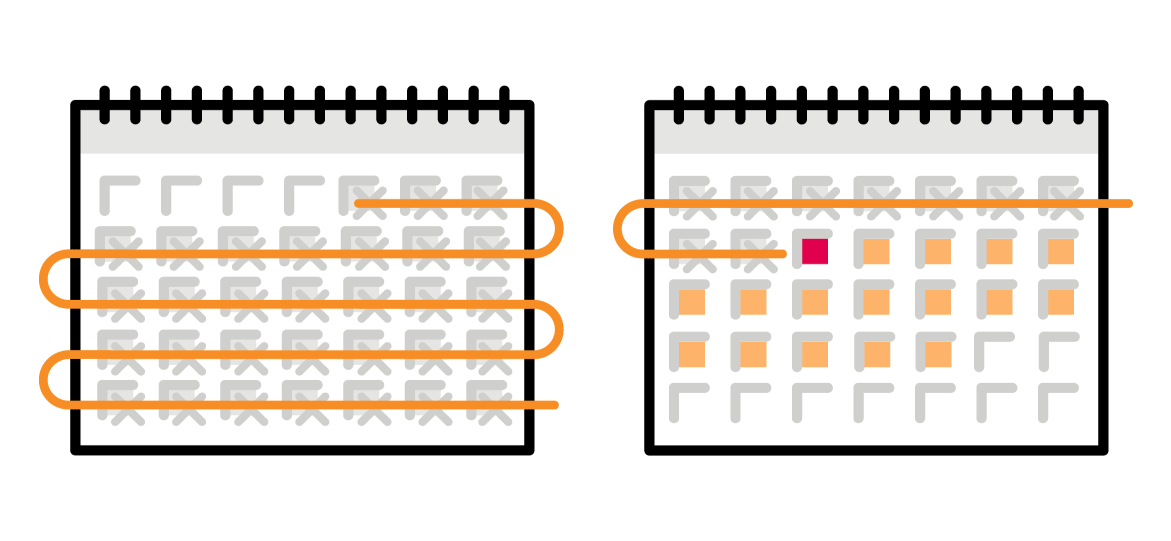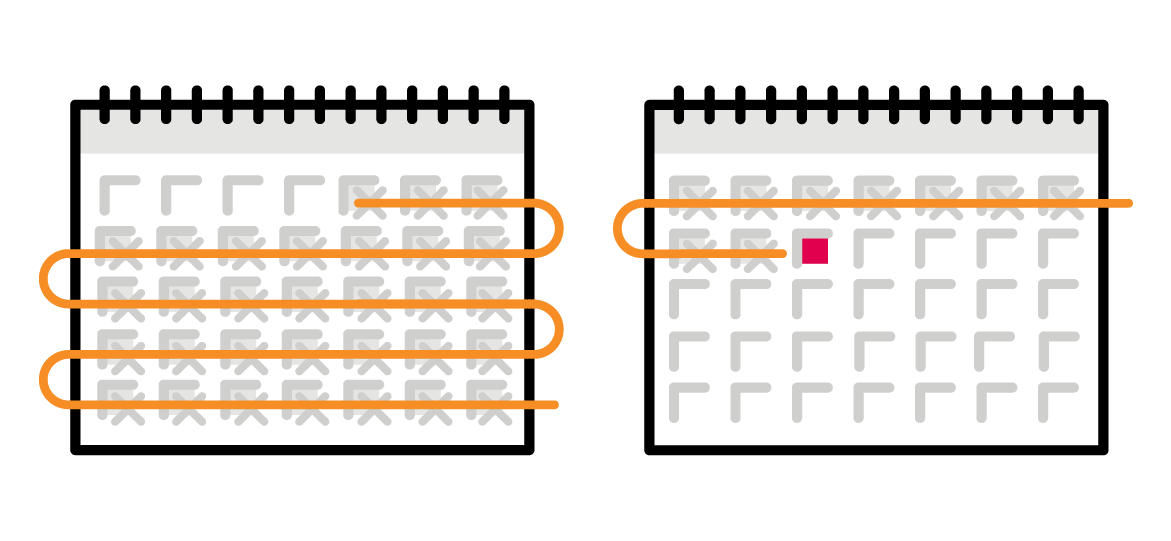
Overall time-to-therapy for this particular neurology specialty product: 6 weeks relative to industry standard 8.3 weeks4 – a 27 percent improvement
*Time referred to in business days
^ While lab test scheduling is coordinated for patients, time to lab completion largely depends on patient availability – a factor outside of AMP control.
Note: As AMP was evaluated for two months after its initial launch, adherence data were unavailable for this study.
Conclusion
During a two-month pilot study, AMP had a positive impact on helping patients to start their prescribed specialty therapy. Relying on the established CoverMyMeds network facilitated rapid conversion of target providers to active AMP users with ~90 percent of providers on the initial, prospective NPI list enrolling over 1,200 patients into AMP services. While electronic enrollment is a change from traditional specialty workflows, nearly half of providers adopted the new technology. The standardized and electronic AMP workflow contributed to short turnaround times, on average, for patient support processes, leading to a 27 percent average decrease in time-to-therapy for patients overall.
While already demonstrating significant improvements relative to traditional patient support models, AMP performance metrics are expected to further improve in the coming months as the program matures and more providers adopt the technology. Additionally, the adherence component of AMP will be evaluated as more patients need prescription refills.
To discover more about how AMP is helping patients to access their specialty medications, visit go.covermymeds.com/specialty
Sources
- Medicine Use and Spending in the U.S., A Review of 2017 and Outlook to 2022, IQVIA Institute, 2018
- The 2018 – 2019 Economic Report on Pharmaceutical Wholesalers and Specialty Distributors, The Drug Channels Institute
- Medicine Use and Spending in the U.S., A Review of 2016 and Outlook to 2022, IQVIA Institute, 2017
- Narrative Review of the Literature on Adherence to Disease-Modifying Therapies Among Patients with Multiple Sclerosis, 2013
- The Impact of Disease-Modifying Therapy Access Barriers on People with Multiple Sclerosis: Mixed-Methods Study, Journal of Medical Internet Research, 2018
- CoverMyMeds Multiple Sclerosis Patient Advisory Board, 2019
- Help for the Patient Journey – Electronic Modernization of Medication Access, Drug Channels Institute, 2019
- Patient Services – Pharma’s Best Kept Secret, Accenture Life Sciences, 2015
- Specialty Pharmacy: Why Does It Take So Long?, Specialty Pharmacy Times, 2017
- Hub Services Special Report 2016, Pharmaceutical Commerce, 2016
- Time-to-Fill: A Standardization Dilemma in Specialty Pharmacy, Specialty Pharmacy Times, 2016